Abstract
Introduction: The growing number of therapies for multiple myeloma (MM) increases the interest in identifying patients more likely to achieve a complete response and longer survival. This post-hoc analysis of two pivotal trials ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR aimed to investigate the profiles of best responders (BRs: complete response or better [CR+]) vs partial responders (PaRs: PR or very good partial response [VGPR]) in the carfilzomib (K) arms, and factors predictive of a CR+ to K-based regimens (carfilzomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone [KRd] or carfilzomib and dexamethasone [Kd] in ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR, respectively).
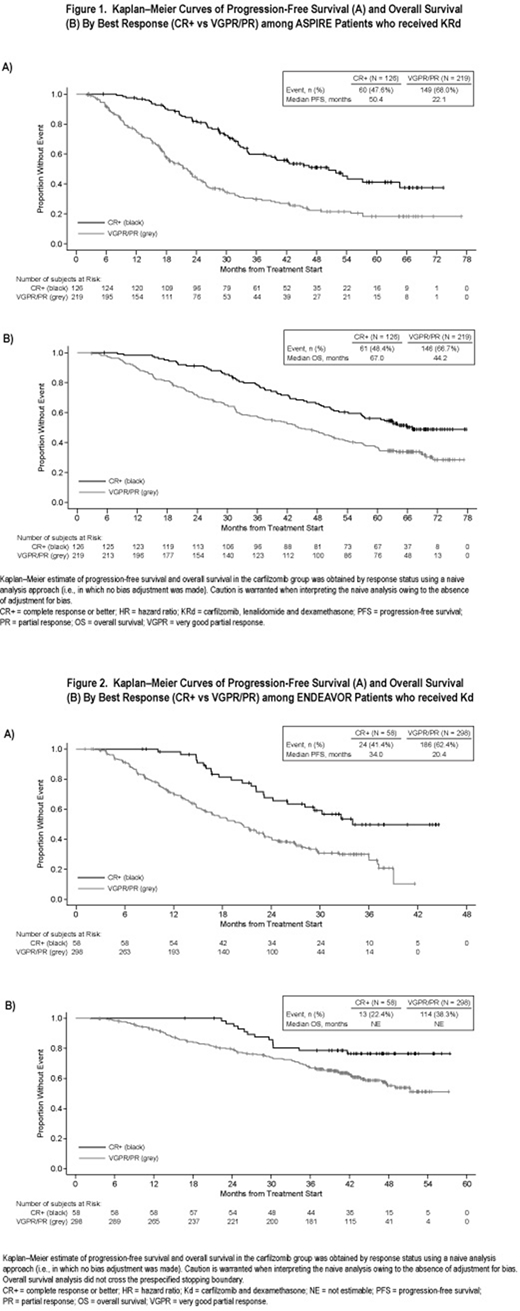
Methods: Response status for this analysis was determined by an independent review committee (as defined in ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR trials). Time to CR+ was calculated as the time from first K dose to the date of CR. Patient demographics and disease characteristics were described by trial for the BR group in the K arms of ASPIRE or ENDEAVOR. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) analyses were based on investigator-assessed data. Kaplan-Meier methodology was used to describe OS and PFS for the BR and PaR subgroups within K arms of each study.
A multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to investigate the relationship between achieving a CR+ and 11 factors defined in a novel, validated risk stratification algorithm (Terpos et al. Hemasphere 2018, PF571).
Safety analyses for best responders included incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), serious AEs (SAEs) and grade 3 or more (Gr3+) AEs and rates of TEAEs leading to discontinuation of K.
The cut-off dates for efficacy and safety analyses were April 28, 2017 and July 19, 2017 for ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR, respectively.
Results: In total, 126 KRd and 58 Kd patients were BRs compared with 219 KRd and 298 Kd patients with a PR/VGPR (PaRs). Demographics of BRs to KRd therapy were: 54.0% male, median age 65 years, 8.7% had an ECOG status ≥2, 11.1% with high cytogenetic risk, and 57.1% had a prior transplant. BRs to Kd therapy were 50.0% male, median age 62 years, 1.7% had an ECOG status ≥2, 25.9% with high cytogenetic risk, and 65.5% had a prior transplant. The median time (Q1, Q3) to CR+ was 6.7 months (4.6, 11.8) for KRd and 6.8 (2.0, 20.8) months for Kd.
The BR group had a longer median PFS and OS than PaRs in each trial (Figures 1 and 2; no adjustment for bias): In the KRd arm of ASPIRE, BRs had a median PFS of 50.4 months vs 22.1 months for PaRs. Among KRd-treated patients, median OS was 67.0 months and 44.2 months for BRs and PaRs, respectively. In the Kd arm of ENDEAVOR, BRs had a median PFS of 34.0 months vs 20.4 months for PaRs. Median OS was not reached for either group of responders to Kd: event rates were 22.4% and 38.3% for BRs and PaRs, respectively.
In ASPIRE and ENDEAVOR, respectively, only LDH levels ≤360 U/L or a non-refractory status to new drugs were found to be associated with best response in KRd patients, whereas ECOG status 0 was predictive of best response in Kd patients (data not shown).
BRs were treated longer than non-CR patients, with a median of 37 cycles (3.0, 80.0) vs 17 cycles (1.0, 82.0) and 17 cycles (4.0, 59.0) vs 10 cycles (1.0, 58.0) for ASPIRE (K withheld after 18 cycles) and ENDEAVOR, respectively. The non-exposure adjusted incidence of Gr3+ TEAEs was similar between BRs and non-CR patients (including VGPR, PR, minimal response, progressive disease, or stable disease) in each trial (88.9 vs 86,1% in ASPIRE; 79.3 vs 82.2% in ENDEAVOR). Although SAEs were higher among BRs vs non-CR patients treated with KRd (73.0% vs 61.7%), the rate of TEAEs leading to discontinuation of K was only 5.6% among the BRs vs 15.0% in non-CR patients. In ENDEAVOR, the incidence of SAEs was lower in BRs compared with non-CR patients (51.7 vs 61.5%, respectively); and the rate of TEAEs leading to discontinuation of K was also lower for BRs (25.9 vs 30.1%, respectively).
Conclusion: A complete response or better was rapidly achieved by 31.8% and 13.0% of KRd and Kd patients, respectively, and translated into better outcomes than partial responders. Surprisingly, although best responders were treated longer with carfilzomib, the discontinuation rates due to TEAEs were lower compared with other patients, which may imply that good management of TEAE preventing discontinuation may allow responders to improve their response to carfilzomib-based therapy over time and likely achieve a deeper response.
Weisel:Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, Juno, Sanofi, and Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, and Sanofi: Research Funding. Mateos:Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gay:Janssen, Amgen, Takeda, Celgene, BMS: Honoraria; Janssen Takeda Celgene, Amgen, BMS, and Roche: Other: Advisor; Abbvie: Consultancy; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Delforge:Amgen, Celgene, Janssen and Takeda: Consultancy; Celgene and Janssen: Research Funding. Cook:Celgene, Janssen and Takeda: Research Funding; Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlycoMimetics, Celgene, Janssen and Takeda and Sanofi: Honoraria. DeCosta:Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Desgraz:Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Szabo:Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Moreau:Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal